1. WHAT IS RATTAN?
Often mixed uo with bamboo or wicker, rattan belongs to the palm family. It attaches itself and climbs to the biggest trees in the rainforest. Some rattan vines can reach up to 300m long. There are more than 300 different varieties with different colors, sizes and localizations. Some can be found in Africa (Cameroun), Amazonia, but Asia is its favorite continent, and Indonesia particularly, where the nicest varieties can be found. The specificity of rattan is its ability to be curved when steamed and, once it has cooled down, to keep the shape that was given. Rattan is the ideal material for curves, curls, rings and is much appreciated for its resistance to humidity and temperature changes. On a single armchair, 3 or 4 rattan varieties can be found, each of them with special features : the structure will be built in a strong rattan, with large diameter, the weaving part in a fibrous rattan, the ligatures in a knot-free variety etc...
 |
 |
 |
| Rattan in its naturel environment | rattan ready to be used | curving rattan |
Where does rattan come from?
Most rattan varieties grows or are cultivated in South-East Asia, mainly in the area around the Borneo rainforests. Farmers go to the jungle everyday and cut all kinds of rattan. The collected vines are weighted and paid every night then brought by boat to a sorting site. The women that often work in these companies wash, cut and sort all kinds of rattan that will later be sold to manufacturers across Indonesia.
The richness of soil in this area made it possible to let grow hundreds of varieties, each of them with special features, that we can use for our furniture and baskets. Depending on the place where rattan grows, it can be very dense in the inside, which is perfect for structures, or very soft, which is perfect for weaving or decoration. Diameters range from 2 to 50mm... with numerous possibilities. The natural color also range from straw-coloured yellow to dark brown, also depending on the area where it grows. Nonetheless, rattan skin can be removed, peeled. The core absorbs al kinds of colors and lacquers, allowing all kinds of designs.
What is the difference between bamboo?
Bamboo is often mixed up with rattan when it comes as sticks. Same yellowish skin color when dried, round knots... The main difference is that bamboo has a hollow trunk while rattan is solid. Bamboo is very stiff, it is even used to build scaffolding in Asia, but it is impossible to bend. It is also usually wider than rattan. Some furniture are also made in bamboo, but only with straight designs.
Bamboo = straight and stiff vs. rattan = curved and flexible.
What is the difference between wicker?
Wicker belongs to the willow family and it usually grows in colder countries. Even when it comes from China, it is from Northern China. It is often used as weaving material for chairs or baskets. But it is too thin to make a structure. It is easy to mix up rattan and wicker when wicker is whiten. Yet, it is smoother and shinier. In France, wicker is usually found in "Haute-Marne", "Touraine" and "Somme" regions, even if it can grows in all humid and cold places.
2. MANUFACTURING RATTAN
 |
 |
 |
| Cutting rattan in the rainforest | hot bath where parasits are killed | open air drying |
 |
 |
 |
| peeling rattan | canes are placed in steam tubes... | ... so it can be curved easily |
 |
 |
 |
| It is a real know-how ! | Templates help the bending part | Assembling... |
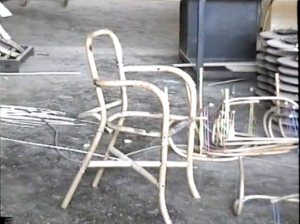 |
 |
 |
| ... and here is the structure ! | The ligatures | Weaving is directly made on structures |
 |
 |
|
| same technics for baskets | Last check |
3. MAINTENANCE
How to take care of rattan?
Regularly remove dust with cloth or the vacuum cleaner brush.
For the baskets or weaving parts of furniture, brush them carefully with hot salted water. Rince well with cold water and let dry.
After a whole winter in the garage, rattan furniture may be very dirty. After a quick cleaning with a humid cloth, brush them with soft soap diluted in hot water. Once dry, apply linseed oil with brush.
Can rattan stay in the garden?
Rattan is absolutely not guaranteed for outdoors use. It is natural material: colors fades with sun and it will be attacked by micro-organisms and mould if it stays in the garden under rains or worse, frost.
Rattan can spend summers in the garden and bear a small rain, especially if it still has its skin. Like Parisian cafes, always bring them back indoors the rest of the year and keep them in a cold place. Rattan can bear humidity and temperature contrasts in the house, which make it perfect material for conservatory and winter garden.
It is possible to wash furniture and basket fabrics?
The fabrics used for our products is 100% cotton. you can wash it at max. 30°C. It is easier to put the cushion covers back when they are still humid.
4. GLOSSARY
What is rattan core?
It is the hearth of a rattan stick (which is solid, unlike bamboo). It can be cut, a bit like spaghetti, in several small filaments, usually rond shaped, from 2mm to 8mm, and meters long. These wires are used for baskets or armchairs weaving. It can be found as is in the market, usually in a wreath shape. As rattan core, it has a fibrous look and has no skin. It is perfect for paint and lacquer, just like raw wood.
What is "Tohiti" rattan?
"Tohiti"rattan comes from the Sumatra island in Indonesia. Its diameter ranges from 10 to 32 mm and its length can reach 200 meters. Its main characteristics is it solid skin and flexible core. It is a very good variety that we use mainly for our seats structures. Once steamed and placed over a template, it stays in the desired shape when it becomes cold.
What is rattan "Strands"?
Rattan "Strands" is the name of the peeled bark of rattan. It comes as a lace and is usually used for ligatures and flat weaving patterns. The silica contained in the bark makes a very strong material. The best strands, from knots-less rattan varieties, are used to make the "French rattan patterns" of classical seats.
